Many women are worried about putting on excess weight during pregnancy. The most common questions are how to lose weight during pregnancy safely without hurting the health of herself and growing baby. What is the optimum weight that I should/will put on during pregnancy? Is it possible to lose weight during pregnancy if I am already overweight or obese? What are risk factors of being overweight or obese while pregnancy?
Well, gaining weight during pregnancy is quite normal and you should not worry about it. The weight you put on during pregnancy is not fat, it is related to the growing baby. Your body is becoming ready for accommodating the growing baby. The energy requirement for your body also becomes more than that as it was before. So, you require at least 300 extra calories a day than what you need before being pregnant. Therefore, dieting or restricting any food during pregnancy is not good for your health. However, you can choose healthy foods and balanced diet to keep your weight under control. So, it is possible to maintain weight and reduce weight as long as your diet is fulfilling the energy requirement for you and your growing baby.
Normal Weight Gain during Pregnancy
The main question of how much weight I will gain during pregnancy. Let’s start discussing it first.
Gaining weight during pregnancy depends on your category of pre-pregnancy BMI. Based on BMI, the recommended weight gain is shown in the table below:
| Category | Pre-pregnancy BMI | Weight Gain |
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 | 13 to 18 Kg |
| Normal | 18.5 to 24.9 | 11 to 16 Kg |
| Overweight | 25 to 29.9 | 7 to 11 Kg |
| Obese | Above 30 | 5 to 9 Kg |
If you have twin or multiple babies, then your recommended weight gain is between 16.5 to 24.5 Kg.
Note: If you already overweight or obese, then your doctor may recommend losing weight.
Causes of Natural Weight Gain during Pregnancy

Pregnant Woman
Pregnant women gain weight because it adds up the weight of the baby, placenta, amniotic fluid, breast tissue, fat stores, uterus growth and blood supply to the baby. Here is a breakdown for 16 Kg weight adds up during normal pregnancy and in women with normal pre-pregnancy BMI.
| Baby | 2.5 to 3.5 Kg (5 to 8 lb.) |
| Placenta | 1 to 1.5 Kg (2 to 4 lb.) |
| Amniotic fluid | 1 to 1.5 Kg (2 to 4 lb.) |
| Breast tissue | 1 to 1.5 Kg (2 to 4 lb.) |
| Fat stores | 2.5 to 4 Kg (5 to 9 lb.) |
| Uterus growth | 1 to 2.5 Kg (2 to 5 lb.) |
| Blood supply | 2 Kg (4 lb.) |
Risk factors of being Overweight or Obese during Pregnancy
If a pregnant woman is overweight or obese, it gives rise to several health risk factors. It may lead to the following complication during pregnancy.
Preeclampsia
In the developed countries including the USA, obesity is epidemic among women. Around 60% of women have BMI above 25 and some of them have BMI over 30. The obesity increases the risk of pre-eclampsia by 3 times. The higher BMI leads to a higher risk of preeclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia also increases the risk of stroke, premature birth and other complications.
Gestational diabetes
Overweight and obese women have 4 times more risk of developing gestational diabetes than women have normal BMI. Gestational diabetes (GD) increases the risk of having large babies and congenital disabilities. Therefore, the most of women with GD require a cesarean delivery.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is common in overweight and obese people. Pregnancy can worsen the problem of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA can increase the risks of preeclampsia and cesarean delivery. Furthermore, newborn babies may also require neonatal intensive care.
Other Problems
Being overweight or obese during pregnancy also increases the risk of following health problems:
- Infections: overweight or obese women have a higher risk of infections during and after pregnancy.
- Problems during labor: the most obese women require induction for labor. Sometimes, obese women need higher doses of oxytocin, which increases the chances of having a c-section
- Obesity also increases the risk of post-partum hemorrhage, higher perinatal mortality and morbidity and may extend hospital stay.
- Overweight and obese women have a higher risk of developing complications in their babies. Obesity increases 60% higher risk of hydrocephalus, 30% higher risk of heart defects, and 20% higher risks of the cleft lip in babies born to obese women than babies born to normal women.
- Overweight and obese pregnant women may also experience more physical symptoms including headache, backache, heartburn and excess pelvic pressure than women having normal BMI.
Well, obese women want to lose weight after knowing all these things. Every woman wants to prevent all these problems and give birth to a healthy baby. However, they are also concerned about how safe is to lose weight during pregnancy. Which things are safe and which things should not be done. Who should try to maintain weight or lose weight? In next section of the article, we are covering all these aspects.
- Women with normal BMI don’t require to worry about losing weight. Gaining weight during pregnancy is healthy for them. However, they should take the healthy and nutritional diet.
- Women who are overweight and have BMI higher than 25 should try to keep weight under control. Women with BMI above 30 should try to lose weight. However, it should only be achieved with healthy and nutritious diet and lifestyle changes.
- Also, it is required to check how much weight gain during pregnancy is normal for you. Check it above in the table under heading “Normal Weight Gain during Pregnancy”. You should not worry about that.
Warning: In the most cases, pregnant women should not lose weight or restrict diet intake. It can be dangerous to their health. It is the best to try for losing weight before you conceive a baby. Everything that you do for maintaining weight, you should do under the supervision of a dietitian and physician that have expertise in pregnancy diet.
What can we do if we are not allowed to lose weight during pregnancy? We can only improve diet and lifestyle to maintain weight. It includes taking care of your calorie intake and its actual requirement, restricting refine sugar and sugar products and eating more fruits, vegetables, products made of whole grains, etc.
Perfect Time to Lose Weight during Pregnancy
Your body naturally gains weight during pregnancy. During second and third trimesters, you will likely to gain more weight. In the last 2 months of pregnancy, baby grows rapidly. So, you will gain more weight during last 2 months. During last 2 months, you must not try to lose weight or restrict your diet. It might be dangerous for your health and baby too. You cannot stop gaining weight that attributed to mass gain by the baby and supporting structures like placenta, amniotic fluid etc. Your purpose should not be losing weight that you attain as the outcome of pregnancy. You should think about controlling weight earlier in the pregnancy, even before you start trying to conceive.
How to Lose Weight during Pregnancy safely
The research studies suggest maintaining and losing weight during pregnancy for overweight and obese women is possible and even helpful for getting better maternal and neonatal outcomes. Here are healthy tips for maintaining weight during pregnancy at optimum and recommended level.
Quick Tips
- Focus on healthy eating habits.
- Keep a check on your actual calorie intake and recommended calories requirement.
- Choose right foods and eat a nutritious
- Try to stay active and do recommended exercises during pregnancy.
Check Calorie Intake
First, you should know how many calories you need during pregnancy.
Recommended Calorie Intake during Pregnancy
For a healthy pregnancy, a pregnant woman requires nutrition rich balanced diet and moderate exercise (walking, swimming, etc.). The total calories recommendation a day also varies according to different stages of pregnancy. Taking these things into consideration, the recommendation for total calories intake per day for a pregnant woman is given below:
| Trimester | Calories per day |
| 1st Trimester | 1800 calories |
| 2nd Trimester | 2200 calories |
| 3rd Trimester | 2400 calories |
Above table suggests calorie intake required per day according to your stage of pregnancy. If you are taking more than that, you should think to reduce calorie intake.
Minimum Calorie Requirement
Never eat less than 1700 calories per day. These are a minimum number of calories require for getting sufficient energy for you and your baby. Taking less than 1700 calories per day, you may also lack important nutrients required for optimal growth of the baby.
Tips
- Track your food intake and note down calories in that.
- Above table provides a general reference. You also need to talk with your doctor to know how many calories you should consume a day. Because all pregnant women may have a different
- Don’t follow any specific diet design to lose weight including low-carb diet etc. It may be dangerous instead of providing benefits.
- Just check if you are taking more calories than as recommended by your healthcare If so, you should reduce it and adhere to the recommendation of your doctor.
- You should also talk to a dietitian to discuss a food plan. Your dietitian can provide your customized food plan for your calorie requirement. Ask for a monthly plan.
- Eat frequent but small meals.
Dietary Guidelines
The following dietary guidelines can help you in choosing the healthy diet. These guidelines will also help to keep your weight under control.
Eat More Vegetables, Fruits & Salad

Fruits and Salad
Eat a good amount of vegetables, fruits and salad. It will provide an abundant amount of nutrients required for a healthy pregnancy. It also helps to reduce food craving and prevent excess calorie intake from other foods.
Choose Healthy Fats
During pregnancy, you need 35% calories intake from fats. Total recommended fat intake per day is 70 grams from which 50 grams should be from unsaturated fats and 20 grams should be from saturated fats. Cut out unhealthy fats especially fats from animal origin (e.g. meat) and try plant-based fats.
Healthy Fats
The following oils and fat sources are considered healthy.
- Avocados
- Coconut Oil
- Olive oil
- Pine nuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Ghee (clarified butter)
- Butter – 5-10 grams per day is fine.
Reduce Intake of following oils and fats
- Hydrogenated vegetable oil – stop it because it is unhealthy fat and very high in Trans Fat.
- Genetically modified oils – restrict intake of canola oil, peanut oil, corn oil and soybean oil
- Oily fish – although it is a good source of omega 3 fatty acids, but it may have a high level of mercury content. So, it is best to avoid it during pregnancy.
Beverages
- Stop drinking juices, especially pre-packed juice. Instead, eat more fruits.
- Stop drinking cold drinks, soda or energy drinks. Choose water instead.
Avoid Junk Foods
Stop eating junk foods like chips and outside food that contains high calories from bad fats.
Exercise
There is a common myth that pregnant women should not do exercise. Because it can be harmful to the baby. It is not true.
Regular exercise is an important requirement for pregnant women. However, it is also an important thing to know which exercises you can do and which are not suitable for pregnant women.
Benefits of Exercise during Pregnancy
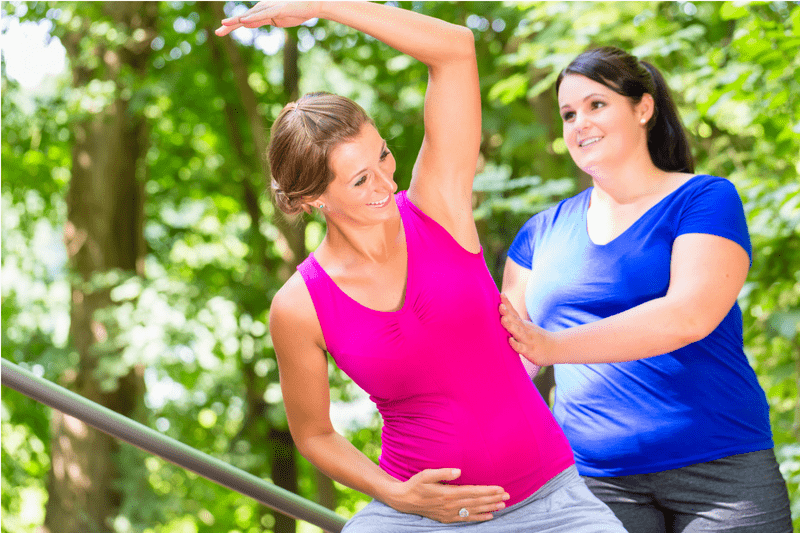
Exercise during Pregnancy
- It helps to maintain weight.
- It lowers the risk of birth defects.
- It reduces backache, bloating and constipation.
- It improves mood and boosts energy level.
- It helps to prevent gestational diabetes.
- It increases muscle tone, improves strength and increases endurance.
- It improves quality of sleep.
Pregnant women also stay fit with regular exercise. Exercise also boosts endurance that helps to cope with labor. After delivery, it also helps to attain pre-pregnancy shape earlier than women who don’t exercise during pregnancy.
How much exercise does pregnant woman need?
The recommendation is not different for a pregnant woman. A pregnant woman also requires at least 30 minutes of exercise per day.
Best exercises for pregnant women
- Walking
- Swimming
- Jogging
- Prenatal yoga
Avoid the following exercises
- That requires maintaining balance including skiing and bike riding.
- That causes pain or dizziness.
- That is done on the back (avoid these after 1st trimester).
References
- Robert Resnik, Robert K. Creasy, Jay D. Lams, Charles J. Lockwood, Thomas Moore, Michael F Greene, Creasy and Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 7th edition, 2014, Chapter 10
- Steven G. Gabbe, Jennifer R. Niebyl, Joe Leigh Simpson, Mark B Landon, Henry L Galan, Eric R. M. Jauniaux, Deborah A Driscoll, Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies, 7th Edition, Chapter 7
- Wang Y, Beydoun MA, Liang L, Caballero B, Kumanyika SK. Will all Americans become overweight or obese? Estimating the progression and cost of the US obesity epidemic. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18719634)
- Bodnar LM, Ness RB, Markovic N, Roberts JM. The risk of preeclampsia rises with increasing pre-pregnancy body mass index. Annals of Epidemiology (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16029839)
- Louis J, Auckley D, Miladinovic B, Shepherd A, Mencin P, Kumar D, Mercer B, Redline S., Perinatal outcomes associated with obstructive sleep apnea in obese pregnant women, Obstet. Gynecol. 2012 Nov. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23090526)
- Kobayashi N1, Lim BH2, Induction of labor and intrapartum care in obese women, Best Practice & Research: Clinical Obstetrics & Gynecology, 2015 April. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25441151)
- Liu, J., Wilcox, S., Whitaker, K. et al. Maternal Child Health Journal (2015) 19: 840. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-014-1582-0)
- Sara Holton, Christine East, Jane Fisher, Weight management during pregnancy: a qualitative study of women’s and care providers’ experiences and perspectives, BMC Pregnancy Childbirth (2017), (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5637069/)
- Nascimento SL, Surita FG, Cecatti JG., Physical exercise during pregnancy: a systematic review., Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. (2012) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23014142)

