Ayurveda is the oldest known form of medical system and it originated in ancient India. Today after so many years Ayurveda is still used by millions of people around the globe. Ayurvedic treatments not only help your body but also develop a type of connection between humans and Mother Nature, – Earth.
What is Panchakarma Detoxification?
Panchakarma is a type of healing and detoxifying process mentioned in Ayurveda texts. The word ‘Panchakarma’ is derived from Sanskrit word, which means ‘five therapies’ or ‘five actions’. It is a body purification therapy that helps in maintaining a peaceful balance between the body, soul and mind.
In Ayurveda, there are three types of Doshas or Humours, which refer to the various emotional and physical functions and its imbalances. These Doshas are:
- vata,
- pitta
- kapha
Panchakarma is a rejuvenating process which aims at removing all body deeply rooted metabolic toxins that may in the future lead to an illness. In other words Panchakarma is amid to evacuate specific morbid Dosha from the body.
Modern lifestyle has led to problems like stress, emotional instability, and poor eating habits, obesity, a lifestyle disease, poor digestion, inefficient immunity, hormonal imbalances and lack of physical exercises, which disturb the balance in the body and mind.
So such complete cleansing detox permits the biological system to gain homeostasis, and to rejuvenate quickly and also eases the desire pharmaco-therapeutic effects of medicine.
Panchakarma is best suggested for people suffering from some chronic illness. Panchakama is also done regularly once a year for someone who is already healthy and wants to keep his body and mind in harmony. So Panchakarma is complete promotive, preventive and curative procedure.
How Panchakarma works for chronic disease?
All chronic disorders are associated with low immunity, weakness of digestive fire, extreme vitiation of micro channels, and improper nourishment of tissues. Panchakama detoxification effectively eradicates toxins, metabolites and stagnated excreta from the body. It improves the digestive fire and finally ejects the morbid Doshas from the body.
It purifies the micro and macro channels, boosts the nutrients absorptions and metabolism, which in returns helps nutrients, medicine and energy to flow freely in the body. This bio- purification makes the biological system to return to normal and to restore rapidly.

Things needed for Panchakarma
Before going for panchakarma detoxification it is advised to prepare body for the process. You need to make sure that you are consulting a qualified and trained ayurvedic practitioner. The practitioner will first take note of all your health issues during ayurvedic consultation. Consultation will cover the details of related health problems both previous and present, any type of mental or emotional instability. This part is very important in the treatment because Panchakarma procedures are based on the special needs of your body.
What Panchakarma involves?
Panchakarma detoxification involves various procedures along with changes in diet and exercise schedules. You may be advised to practice specific yoga or meditation on daily basis to keep your mind fresh. During the whole therapy, you need to take very simple diet, which would involve vegetables, khichari and ghee or other edible oils. The process of Panchakarma involves the following types of stages:
- Preliminary stage (Purva karma)
- Primary stage (Pradhana karma)
- Follow-up stage (Pashchat karma)
Further each stages consists of following Panchakarma therapies:
Preliminary stage (Purva karma):
- Deepana therapy– Increasing digestive fire or metabolic appetite
- Pachana therapy– Digestion of undigested food or toxins
- Snehana therapy – Oleation therapy
- Swedana therapy – Steam or sudation therapy
Primary stage (Pradhana karma):
- Basti – herbal or oil enemas
- Nasya – nasal therapy.
- Virechana – purgation therapy
- Vamana – emesis therapy.
- Raktamokshana – bloodletting therapy.
Follow-up stage (Pashchat karma):
- Rejuvenating therapy
- Aphrodisiac therapy

The combination of this procedure may vary depending upon the various needs and conditions of the patients. Your practitioner is the one who will decide the type of therapies and the period for which you would need it.
Before going for Panchakarma therapy, you are advised to make up your mind because some procedures may be very challenging for some individuals. You also need to make changes in your diet, a few weeks before the starting of the treatment. The consumption of unhealthy food and meat is highly prohibited. You also need to increase the intake of edible oils as it helps in the easy flow out of toxins from your body. A few processes involved in the therapy are not suitable for children, pregnant women and seniors. Therefore, make sure you understand the procedures before starting the treatment.
Lets discuss some of the Panchakarma therapies in details:
Deepana and Pachana thearpy
Various digestive herbs are given to enhance the digestive fire, which then triggers the mechanism of biotransformation at diverse levels in the body, to expel the toxins and morbid Doshas.
Snehana – Oleation thearpy
Word Snehna refers to imparting oiliness in the body by using different kind of fat or oil. It is administered internally and externally.
Internal Oleation (Snehna)
In internal oleation medicated ghee is given in the morning for 5 to 7 days. The quantity of medicated ghee is increased day by day. It helps to lubricate the body cells and capillaries from internal side. It also makes tissues soft, which becomes suitable for main therapies.
Benefits of Internal Oleation
The main benefits of Internal Oleation are internal lubrication and softening of tissues. In addition, it also helps to treat Vata disorders, excessive thirst, joint pains, weakness, excessive dryness of the skin and mental problems such as insomnia and nervine weakness.
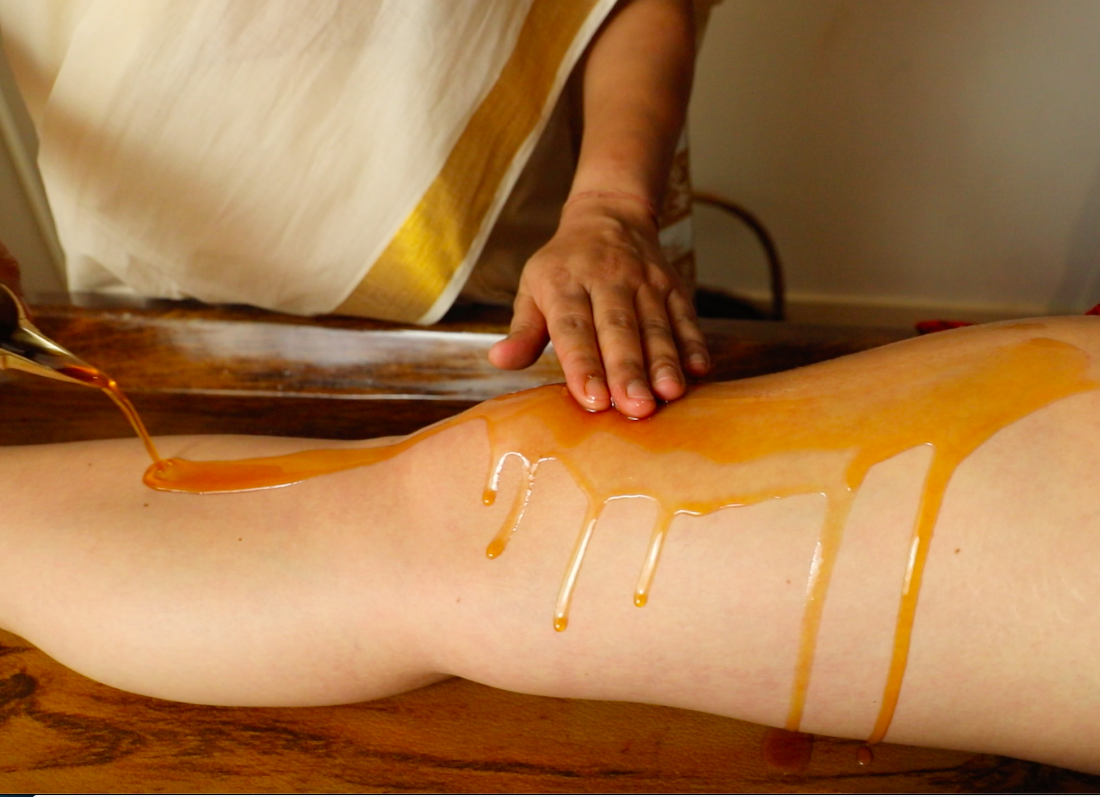
External Oleation (Snehna)
It is a very relaxing therapy, which involves oil ayurvedic massages. These oils are specifically prepared specific to body type of a person.
The oil’s herbs penetrate deep into the skin and nourish the cells. This action helps in inducing circulations in the body and removal of toxic wastes. This also helps the toxins to slip into gastrointestinal track; from there it would be eliminated easily during next stages of Panchakarma. This also leaves skin more nourished; glowing and can also help in avoiding early aging. Moreover it helps to relieve pain, inflammation and stiffness occurring due to any musculoskeletal disorders.
There are several types of techniques used in ayurveda. A few can be read here:
Swedana- Steam or Sudation therapy
In Sanskrit, the word ‘swed’ refers to sweat. The process of swedana refers to the generation of excess sweat to melt and eliminate the toxins from the body. There are many ways in which the body eliminates toxins and sweat is one of them. Swedana is performed to melt the vitiated Doshas, which are spread throughout the body. After a proper sudation therapy, morbid Doshas could easily be expelled out with the help of further stages of Panchakarma.
There are 2 ways of performing this therapy during panchakarma:
- Bashpa Sweda (Sarvanga Swedana)- Complete body sudation
- Nadi Sweda-Sudation on specific body part
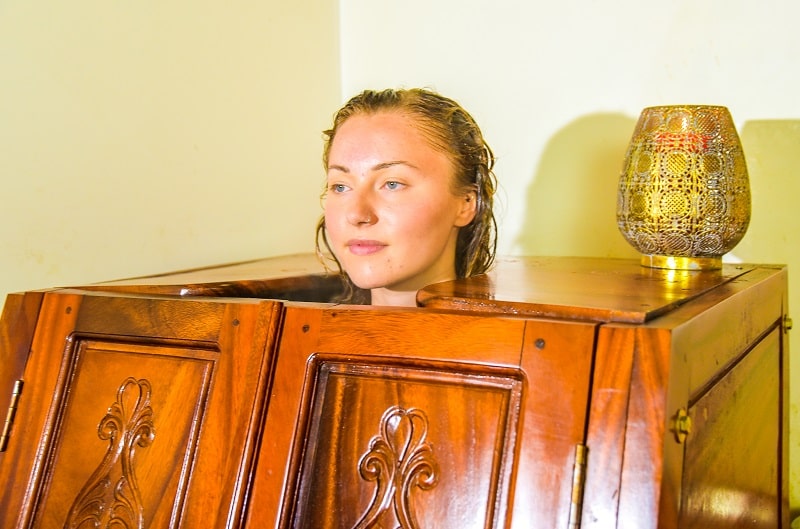

Herbal Steam Bath
Bashpa Sweda refers to the process in which a person is made to sit in a wooden steam chamber, into which medicated herbal steam is introduced, which opens the sweat channels in all parts of the body. It also improves blood circulation, reduces blood pressure, lowers stress and promotes skin health.
Nadi Sweda is a process in which only a few parts of the body are targeted and sweat is generated by exposing that part to steam. It helps in lowering pain, inflammation and stiffness of a part of the body. The most important benefits of Nadi Sweda are that it loosens the stiff joints.
Benefits of Oleation and Swedana therapy:
- It makes the vitiated Doshas (cause of illness) softer and removes its toxins.
- Helps to facilitate the elimination of faeces, urine and sweat.
- Helps the body to become soft and more elastic, and in the removal of stiffness and pain.
- Helps to digest the free radicals or toxins by increasing the cellular and digestive metabolism.
- Oleation therapy increase the oil lubrication in the body channels, and sudation makes the toxins to liquefy into the micro channels, which makes them to move into the main gastrointestinal track, from where it can be expelled easily.
Read More: Nadi Sweda Procedure and its Benefits
Basti- Herbal or oil enemas
Basti is considered one of the most important thearpy in panchakarma treatment. Panchakarma treatments aim at eliminating body toxins. It is the best treatment for Vata Disorders, according to ayurvedic science. Basti is a process in which an enema (liquid or oil solution) is prepared using herbs or medicated oils. This enema eliminates toxins and reduces aggravation of excess vata dosha.
There are two types of Basti Treatment:
Oil Basti
Oil Basti (also called Taila Vasti) is a type of Basti treatment in which only medicated oil is used in enema. It has further type in which a small quantity of oil is used on daily basis. This type of Basti is named as Matra Vasti.
It pacifies Vata dosha and vitalizes the body. In addition, oil basti is also a preparatory therapy that is given before decoction based basti.
Decoction Basti
Decoction Basti (also called Kashaya Vasti or Herbal Basti) is a type of basti therapy in which decoction made of herbs and oils are used together in enema. In addition, rock salt, honey or other natural ingredients may also be used in addition to herbal decoction and medicated oils. It is mainly beneficial in elimination of Doshas and plays an important role in body detoxification.
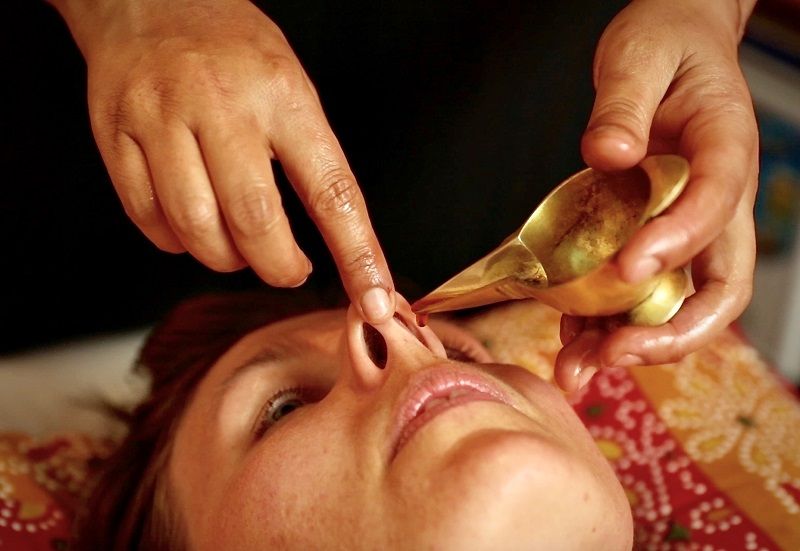

Nasya – Nasal thearpy
Nasya is a procedure specially included for people suffering from nasal congestion, sinuses, respiratory diseases and other allergic conditions. This process includes the pouring of herbal oil drops into the nose directly. This process may also include the inhaling of aromatic herbal steams. This helps in clearing the excess mucus in the nose and helps in fighting dryness in the central nervous system.
Nose is also a gateway to brain. So the medication administered during this therapy is very useful in central nervous system disorders, cervical problems, facial palsy, migraines, trigeminal neuralgia etc.
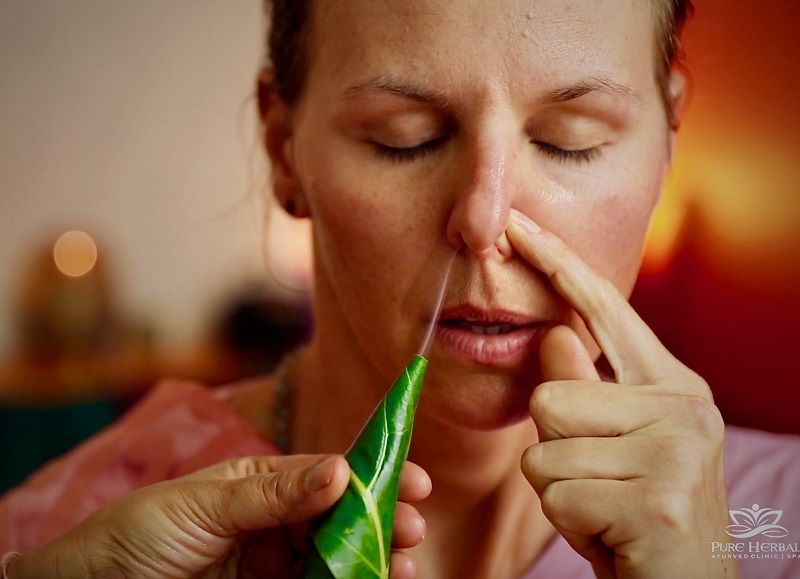

Virechana – Medicated purgation
Virechana is a therapeutic purgation and primary therapy of Panchakarma treatment. It is administrated in cases of aggravated Pitta dosha. It helps in elimination of excess pitta dosha from the body and helps in alleviating symptoms of vitiated Doshas.
It is highly beneficial in toxins elimination, liver and spleen disorders, skin diseases, headaches and gynaecological disorders.
Virechana is intended for purification of the body cells, by which the accumulated morbid Doshas are expelled out to create an perfect atmosphere for appropriate functioning of body.
References
- Conboy, L., Edshteyn, I., & Garivaltis, H. (2009). Ayurveda and Panchakarma: measuring the effects of a holistic health intervention. TheScientificWorldJournal, 9, 272-80. doi:10.1100/tsw.2009.35 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699273/
- Deshpande, S. V., Deshpande, V. S., & Potdar, S. S. (2017). Effect of panchakarma and Ayurvedic treatment in postpartum rheumatoid arthritis (amavata): A case study. Journal of Ayurveda and integrative medicine, 8(1), 42-44. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5377475/
- Patil, V., Baghel, M. S., & Thakar, A. B. (2009). Effect of snehapana (internal oleation ) on lipids: a critical review. Ancient science of life, 29(2), 32-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3336313/
- Patil VC, Thakar AB, Baghel MS. Clinical trial on different dose patterns of Shodhanartha Abhyantara Snehana. Ayu. 2013 Apr;34(2):147-53. doi: 10.4103/0974-8520.119668. PubMed PMID: 24250122; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3821242 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24250122
- Rastogi, S., & Chiappelli, F. (2013). Hemodynamic effects of Sarvanga Swedana (Ayurvedic passive heat therapy): A pilot observational study. Ayu, 34(2), 154-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3821243/
- Gundeti, M. S., Raut, A. A., & Kamat, N. M. (2013). Basti: Does the equipment and method of administration matter?. Journal of Ayurveda and integrative medicine, 4(1), 9-12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3667437/
- Shah, M. R., Mehta, C. S., Shukla, V. D., Dave, A. R., & Bhatt, N. N. (2010). A Clinical study of Matra Vasti and an ayurvedic indigenous compound drug in the management of Sandhigatavata (Osteoarthritis). Ayu, 31(2), 210-7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3215366/
- Rais, A., & Bhatted, S. (2013). Clinical study to evaluate the effect of Virechanakarma on serum electrolytes. Ayu, 34(4), 379-82. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3968700/
- Kaur, M., & Chandola, H. (2012). Role of Virechana Karma in cure and prevention of recurrence of Vicharchika (Eczema). Ayu, 33(4), 505-10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3665194/

